PERHATIAN KEPADA PELAJAR, Sila pastikan anda telah melaksanakan Proses Pengurangan Storan M365 anda. Kegagalan melaksanakan proses tersebut mengakibatkan AKAUN ANDA AKAN DIBEKUKAN.
Akaun identiti yang dibekukan tidak boleh menggunakan perkhidmatan Pearl@USM, Wifi, CampusOnline, M365 dan perkhidmatan yang menggunakan Single Sign On.
Sila pastikan saiz used di Mailbox dan OneDrive anda perlu kurang dari 1GB.
Untuk menyemak saiz storan anda sila rujuk kepada pautan berikut:
Sila rujuk pautan berikut untuk maklumat lanjut:
Jika terdapat sebarang pertanyaan, sila hubungi Servisdesk PPKT di talian 04-653 4400.
Sekian, untuk perhatian dan tindakan segera anda.
Terima kasih.
Please ensure the size of the used space in your Mailbox and OneDrive is less than 1GB.
To check your storage size, please refer to the following link:
Please refer to the following link for more information:
If you have any questions, please contact the PPKT Service Desk at 04-653 4400.
Thank you for your attention and prompt action.
Best regards,

1.Go through the learning material
Make sure you’ve reviewed all the content provided. This will give you a solid foundation for determining which strategies or approaches to use for SIM.
2.Complete the learning activity
Engage with activities first. These are designed to help you relate what you've learned.
3.Complete the self assessment
Engage with the self-assessment by answering all the questions.
This is a learning activity. If you are at this step, you should have completed reading all the learning materials.
Activity: Match the Images
Strategies to support distance learners @SDE
Supporting distance learners requires a strategic approach to ensure they receive the same quality of education and engagement as on-campus students. Distance learners often face unique challenges, such as isolation, time management, and limited access to resources, making it crucial to implement tailored strategies that address these needs.
Unlike traditional classroom settings, distance education demands that instructors consider the unique needs and challenges faced by students who may be studying from various locations, often with limited direct access to instructors and peers. This requires a focus on flexibility, accessibility, and clear communication. By designing courses that are adaptable to different schedules and learning paces, instructors can accommodate the diverse lifestyles and responsibilities of distance learners.
Moreover, without the physical presence of a classroom, students can easily feel isolated or disconnected from the learning process. Therefore, to counter this, it is important for instructors to implement strategies that promote regular interaction, both between students and instructors and among peers.
If you've read the previous topic, you'll already know that an ODL program is quite different from conventional teaching or lectures.
ODL programs offer a more flexible and independent approach to learning, allowing students to study at their own pace and from any location without barriers. It is different from conventional teaching, which takes place in a structured place and face-to-face classroom setting.In ODL, the learning environment is primarily virtual, with students accessing course materials, assignments, and lectures online. This allows learners to study from any location, at any time, making education more accessible to those who cannot attend traditional in-person classes.
ODL emphasizes self-directed learning, where students take more responsibility for their educational progress. They manage their time, engage with materials independently, and often work through content at their own pace.

In conventional settings, learning is typically instructor-led, with a more structured schedule and direct guidance. Students follow a predetermined pace set by the instructor, with less flexibility in how and when they engage with the material.

Instruction in ODL is delivered through various digital platforms, including Learning Management Systems (LMS), video lectures, discussion forums, and other online tools. These resources often include multimedia elements to enhance learning and are designed to be accessed asynchronously.

Instruction in conventional settings is delivered in real-time through lectures, discussions, and classroom activities. The interaction is immediate, allowing for spontaneous questions and in-person engagement.
Interaction in ODL is often asynchronous, with students communicating with instructors and peers through emails, forums, and recorded webex sessions. While there may be opportunities for synchronous interaction, such as face to face intensive course in School of Distance Education, live webinars, or video conferences.

Interaction in conventional teaching is typically synchronous, with real-time discussions, immediate feedback, and face-to-face engagement during lectures and group activities. Lecturers are able to approach their students to give help, explanation or response immediately with 2 ways communication.
One of the biggest advantages of ODL is its flexibility, allowing students to balance their studies with other responsibilities such as work, family, or travel. This mode of learning is particularly beneficial for those who require a more adaptable schedule. Distance learners able to do self-learning in SIM (PEARL Portal). 


You have learned about how ODL is slightly different from conventional teaching/ lecture. Now, we will go to teaching and learning theories. Did you know there are 3 major learning theories that are important for educators to know?
1. Pedagogy (conventional learning)
2. Andragogy (for adult learners - ODL)
3. Heutagogy (for postgraduate and professional)
In SDE context, it is essential to focus on andragogy, which is the theory and practice of teaching adult learners. Andragogy is particularly relevant for ODL because many distance learners are adults who bring unique characteristics, needs, and motivations to their educational experiences

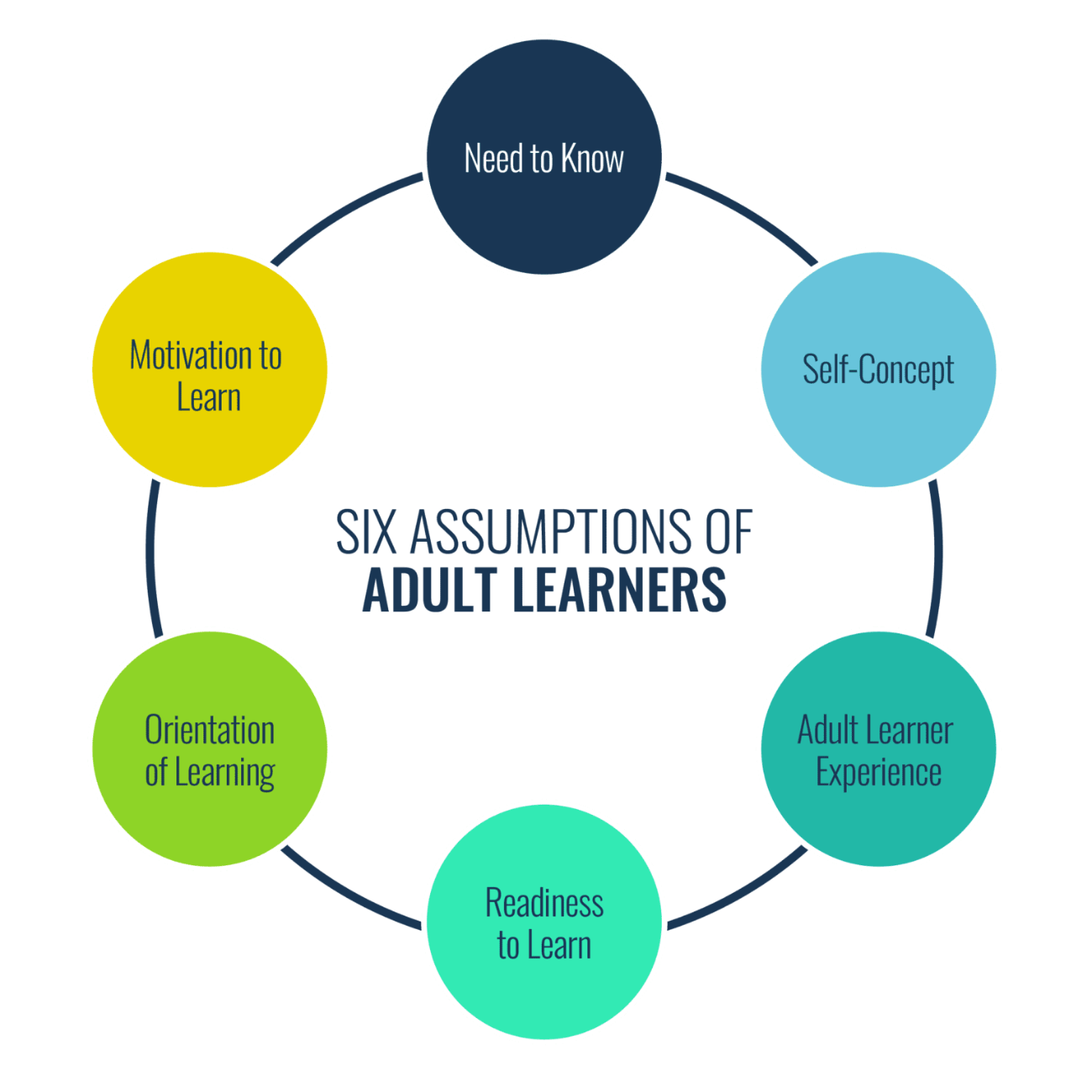
Malcolm Knowles (1913-1977) was a pioneering American educator who brought the term ‘andragogy’ into the spotlight, which refers to the art and science of adult learning. Just as pedagogy focuses on teaching methods for children, adult learning theory explores the ways in which adults learn. This approach has become a cornerstone of adult learning theory and continues to influence how we design learning experiences today. Knowles (1984) also theorized adult learning theory also known as Andragogy. Based on the andragogy, there are 5 assumptions that we need to know when we want to teach adult learners.
Adult learners will learn only believing that learning could aid in solving real life problems. They have diverse experience as learning resource and knowledge from previous experiences (life, work, family etc.,)
Provide course content for the SIM (learning material, activities and assessments)
Structure the content into smaller and manageable parts (Chunks)
Provide instructions in order to give motivation to the learners
Provide learning activities in SIM. Activities must be align with the topical learning outcomes in SIM.
Offer students a way to evaluate their learning outcomes by giving feedback, including answers or solutions, so they can determine whether they were correct or made an error. Self assessments must be align with the intended learning outcomes and bloom taxonomy.
These elements of self-instructional materials (SIM) are based on the instructional science of open distance learning (ODL) and the core principles of instructional design for SIM. They will assist instructors in delivering well-rounded and effective SIM.
All course content that the learners need to learn is provided.
Learners do not need to ask instructor for explanation. Therefore, instructions must be clear and simple to accommodate diverse learners in SIM.
SIM must be flexible and allows self-directed and self-paced learning . Therefore, it is important for content to chunks so that learners can pace their learning according to their schedule.
Content, instructions and learning activities given are engaging and motivating. Relevant to learners’ experience and needs.
Enable the learners to monitor their progress and evaluate their understanding of the content.
Our school's Learning and Technology Support Division offered the Self-Instructional Material Guidelines, which served as the basis for the SIM course plan. When developing a SIM, course managers should be familiar with a few key components. Each component is based on the newest version of the Self-Instructional Material Guidelines, Version 3. Below is a basic outline for the SIM
Topic introduction – gaining attention about the course.
There more components and explanation about the outlines in SIM Guidelines Version 3. It is recommended to course manager to explore the specific guidelines (can be find on additional material).

Many learners enroll for career-related reasons, whether it's to enhance their skills, advance in their current career, or make a career change. They often come from diverse backgrounds and have different levels of capacity when it comes to learning. On top of that, they’re juggling the demands of work, life, and study, making flexibility and support even more important in their learning journey. Course managers working with adult learners need to understand several key aspects to effectively support their success
According to Falasca (2011), adult learners face a range of barriers that can impact their learning experience
External or situational barriers include factors such as aging, health issues, significant life events, and balancing work or social responsibilities, all of which can limit their ability to focus on learning

Internal barriers play a role, such as having a fixed mindset, relying on outdated methods of learning, losing interest in new stimulus, or feeling anxious about their ability to succeed in learning.

These internal and external challenges can significantly affect adult learners' motivation and capacity to learn effectively. However, Falasca (2011) suggests that course managers can overcome these barriers by focusing on creating a positive learning environment and engaging adult learners through
To keep learners engaged and motivated, it's important to strike the right balance between challenge and ease—adjusting the level of tension and degree of difficulty to keep them interested without overwhelming them. Another key is providing specific feedback. Instead of offering general comments, give detailed, personalized feedback that helps learners understand exactly what they're doing well and where they can improve. This way, they feel supported and clear about their progress.
There are recent studies that investigated attrition rate among ODL institution in Malaysia. Most studies aim to identify the factors that contribute to attrition and explore the most effective strategies to reduce attrition rates among online adult learners.